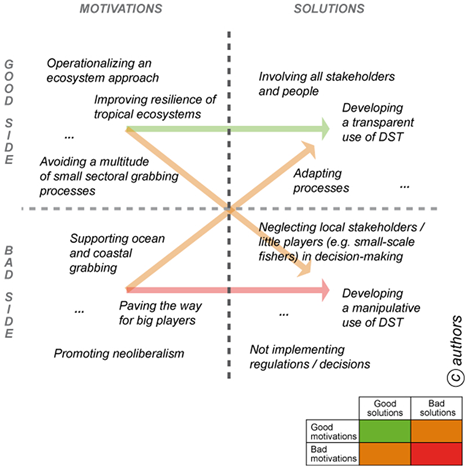
Ocean grabbing occurs when traditional users, such as small-scale fishers, are pushed aside by new development activities. This grabbing must be prevented to avoid sea uses that maintain or increase social inequity. In this paper, we show that in tropical Atlantic countries, such as Brazil and Senegal, examples of ocean grabbing already occur. In this context, we analyse if Maritime Spatial Planning (MSP) may be an opportunity to limit ocean grabbing or, to the contrary, poses a risk to increase it. MSP calls for an ecosystem approach that requires integrated coastal and marine management and involves stakeholders in developing a shared vision of the future, where society and environment are preserved. However, recent studies have shown that MSP is a process to be used cautiously to ensure equitable decisions. Meanwhile, the concept is spreading worldwide including in tropical Atlantic countries. We highlight that context matters and the specificities of the tropical Atlantic must be taken into account when deploying MSP processes. In the tropical Atlantic context, there is increased imbalances of stakeholder power, traps from decision support tools, and a need for adaptive management. These specific features must be addressed when deploying MSP in a way to avoid ocean grabbing.
doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsab006
Reference
Betty Queffelec, Marie Bonnin, Beatrice Ferreira, Sophie Bertrand, Solange Teles Da Silva, Fatou Diouf, Brice Trouillet, Annie Cudennec, Adrien Brunel, Odeline Billant, Hilde Toonen, Marine spatial planning and the risk of ocean grabbing in the tropical Atlantic, ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2021.