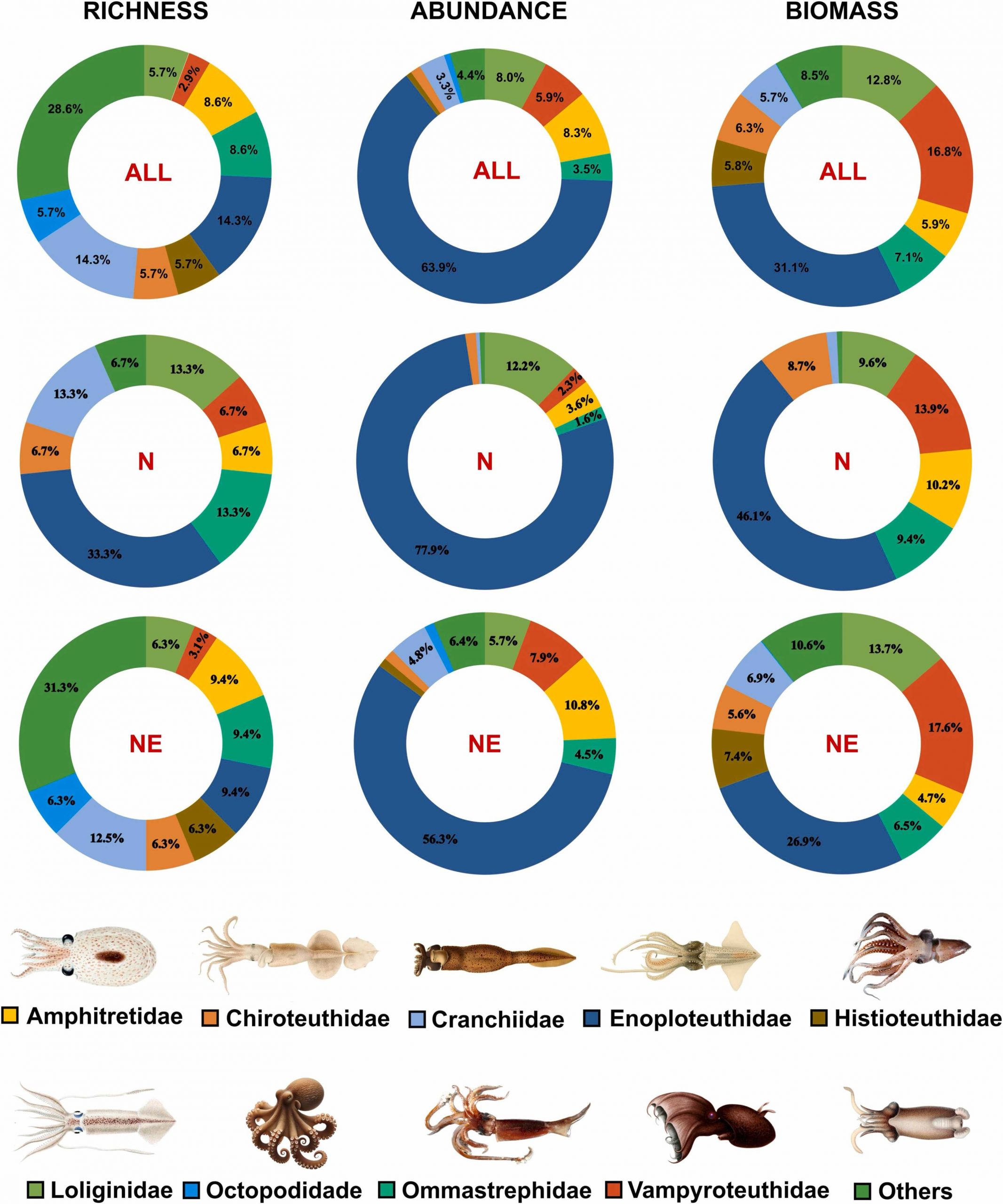
We propose an integrative analysis of the diversity and distribution of pelagic cephalopods collected in the Western Tropical Atlantic (WTA), encompassing the Amazon River mouth
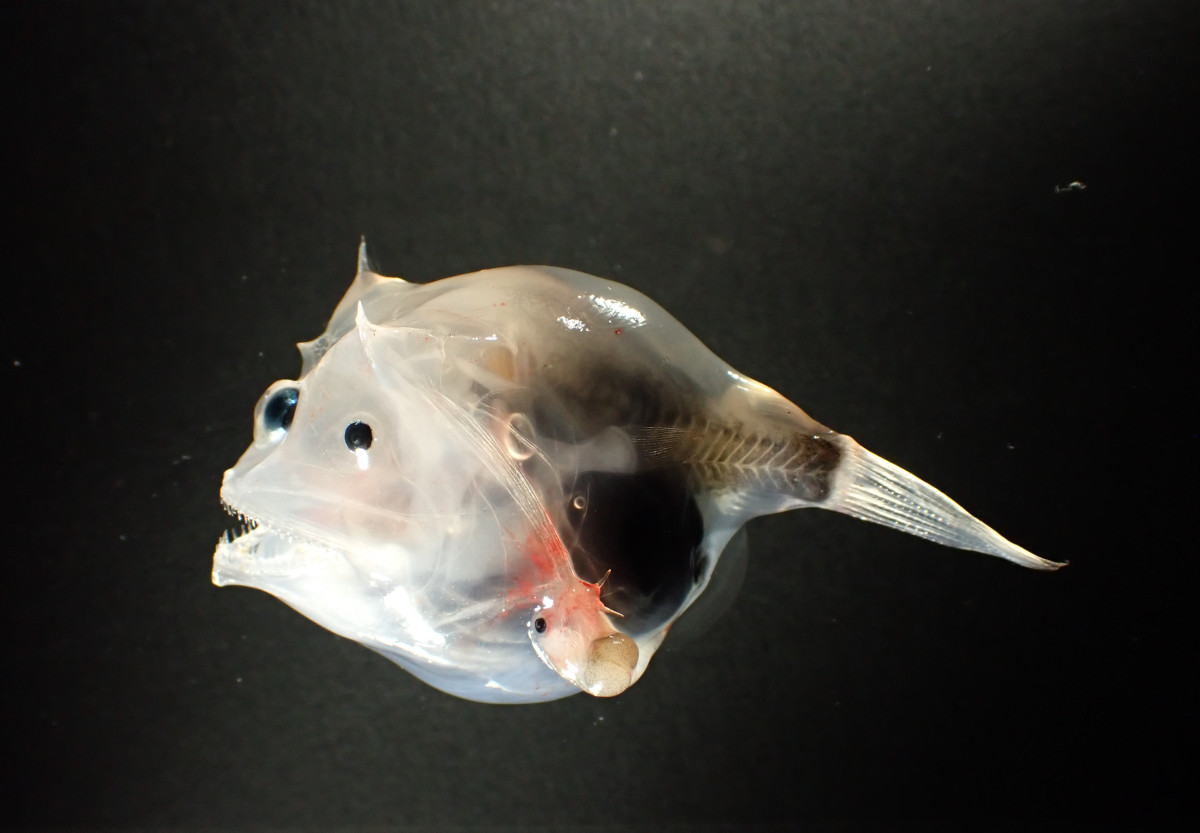
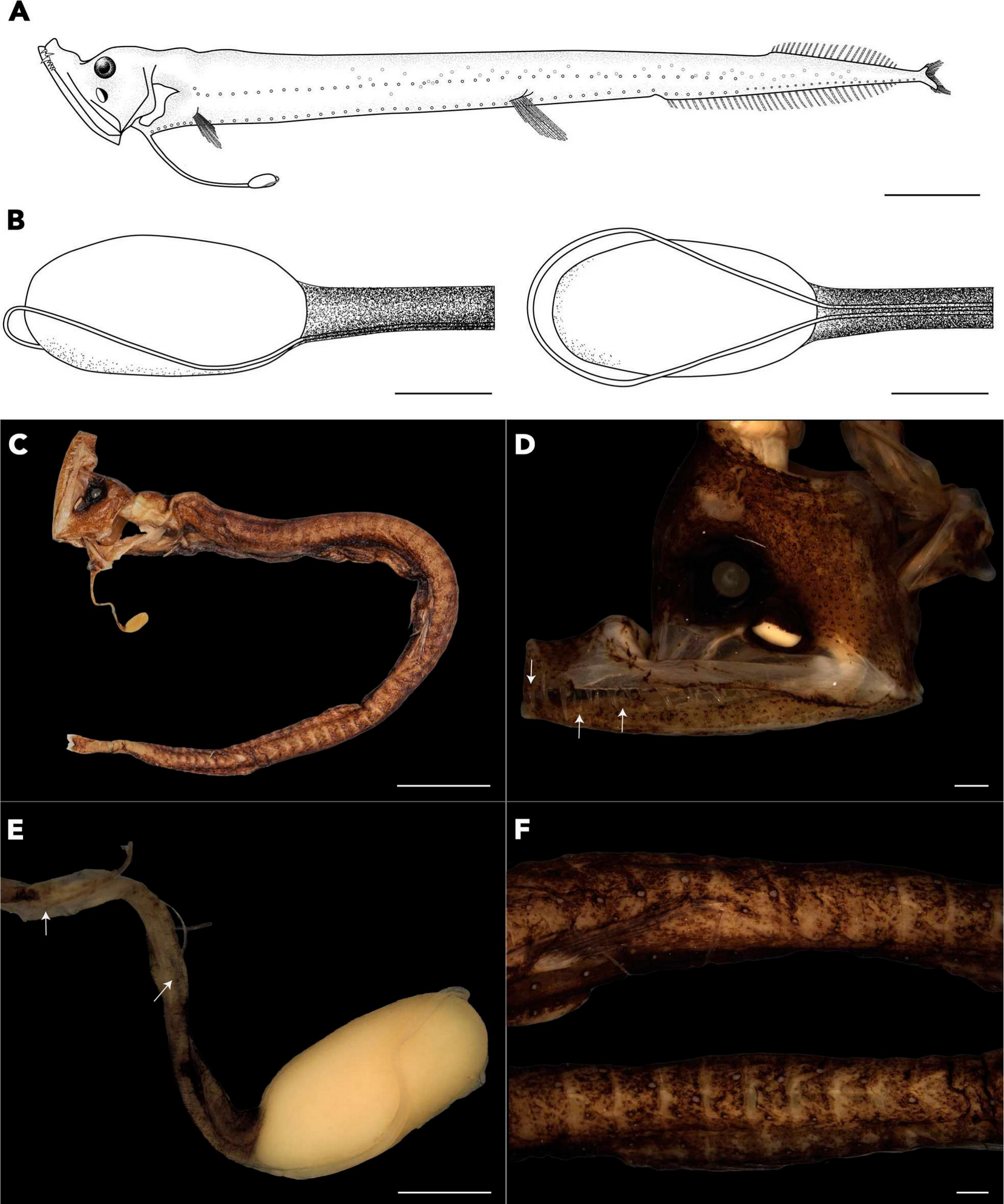
The oceanic anglerfishes (Lophiiformes: Ceratioidei) are among the most diverse and ecologically distinctive groups of deep-sea fishes, exhibiting some of the most extreme morphological adaptations
The exhibition, which brought together art, science, and ocean education, reached diverse audiences on both sides of the Atlantic throughout 2025. The Terra-Mar project, a
A exposição que uniu arte, ciência e educação oceânica alcançou públicos diversificados nos dois lados do Atlântico ao longo de 2025. O projeto Terra-Mar, iniciativa
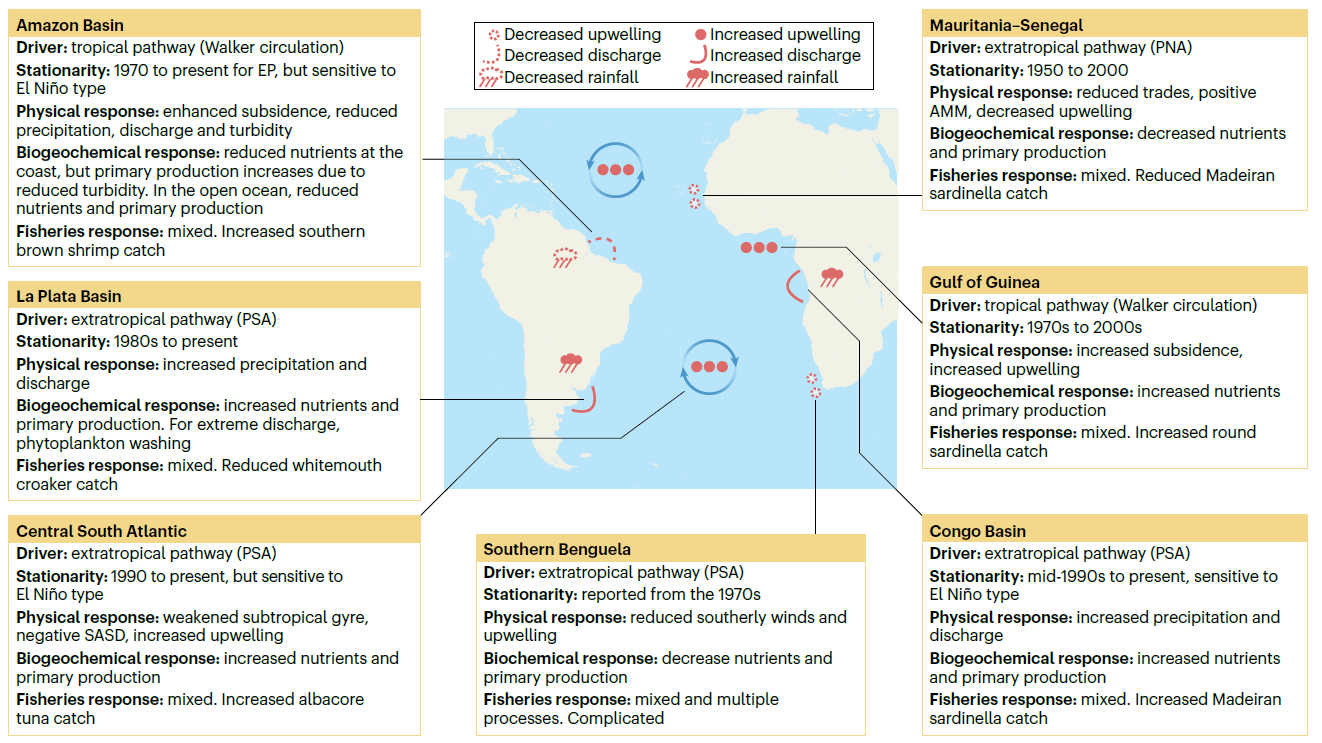
Tropical and South Atlantic marine ecosystems support fisheries that have vital environmental and socioeconomic importance. In this Review, we outline how the El Niño–Southern Oscillation
A new species of scaleless black dragonfish of the genus Eustomias, subgenus Spilostomias, is described based on a single specimen (96.4 mm SL) collected during the ABRACOS
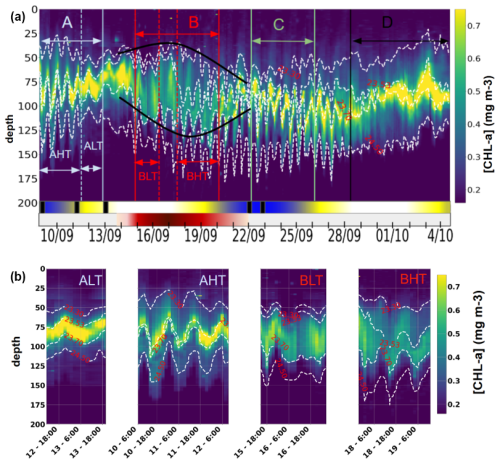
The ocean region off the Amazon shelf including the shelf break presents a hotspot for internal tide (IT) generation, yet its impact on phytoplankton distribution
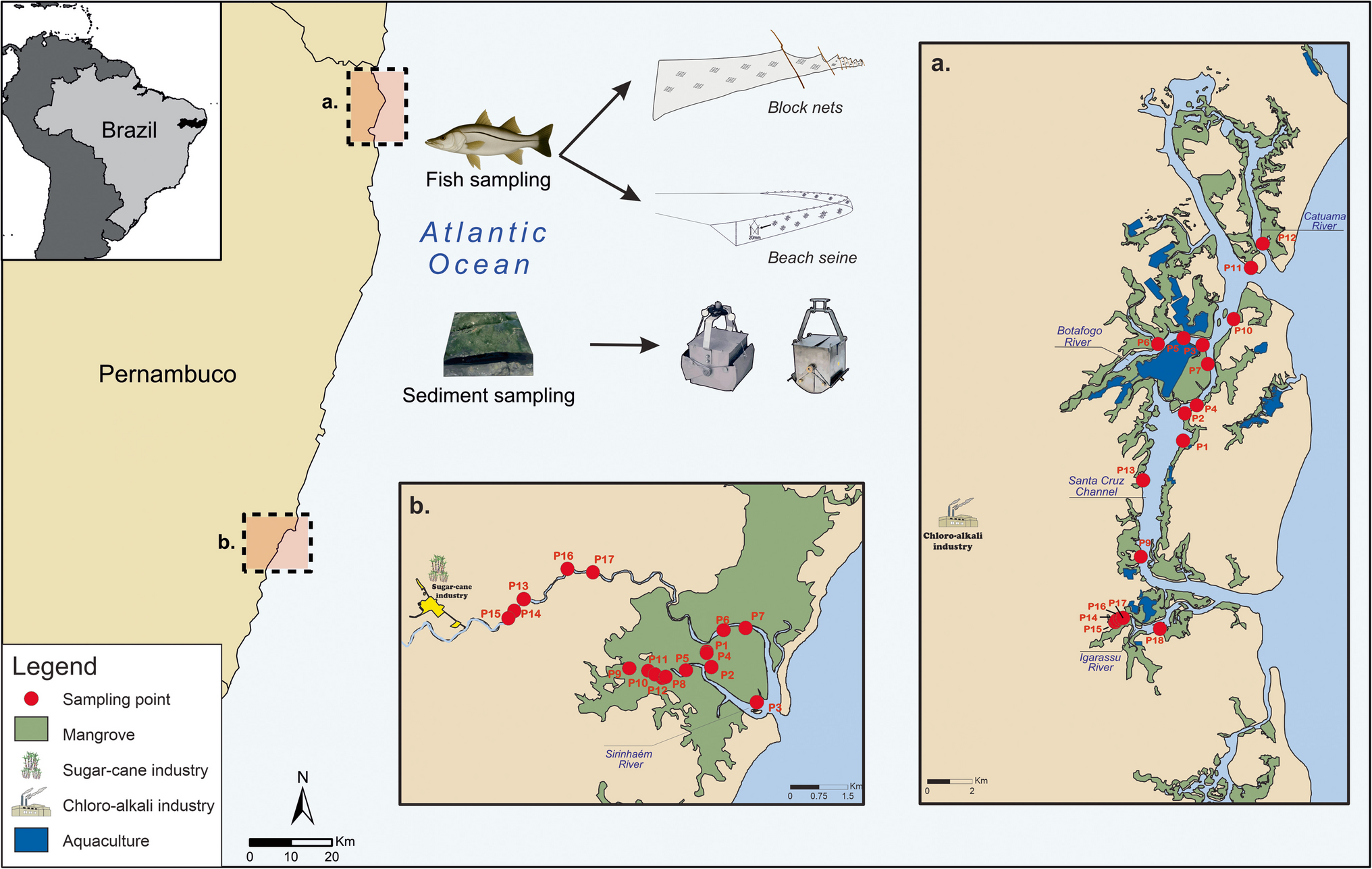
This study evaluated trace metal pollution in sediments and fishes from two tropical estuarine systems in Northeast Brazil: the Santa Cruz Channel Estuary (ITAP) and
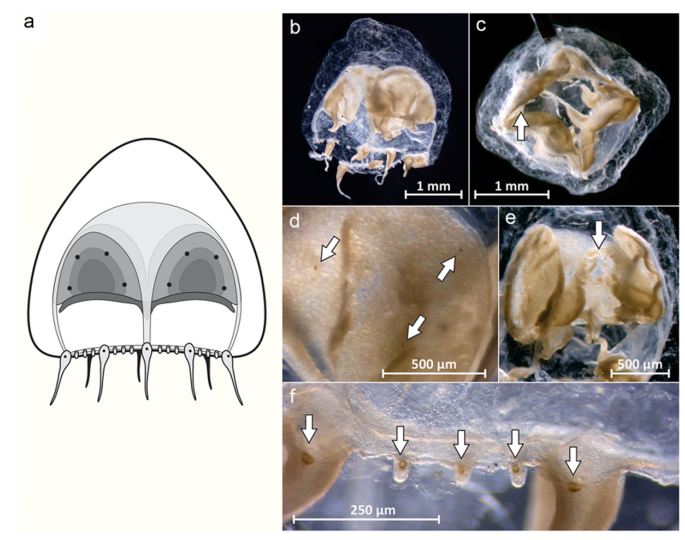
A specimen of the genus Pandeopsis Kramp, 1959 was found in surface waters off the northeast Brazilian coast at 10.93°S, 36.48°W. The specimen was assigned
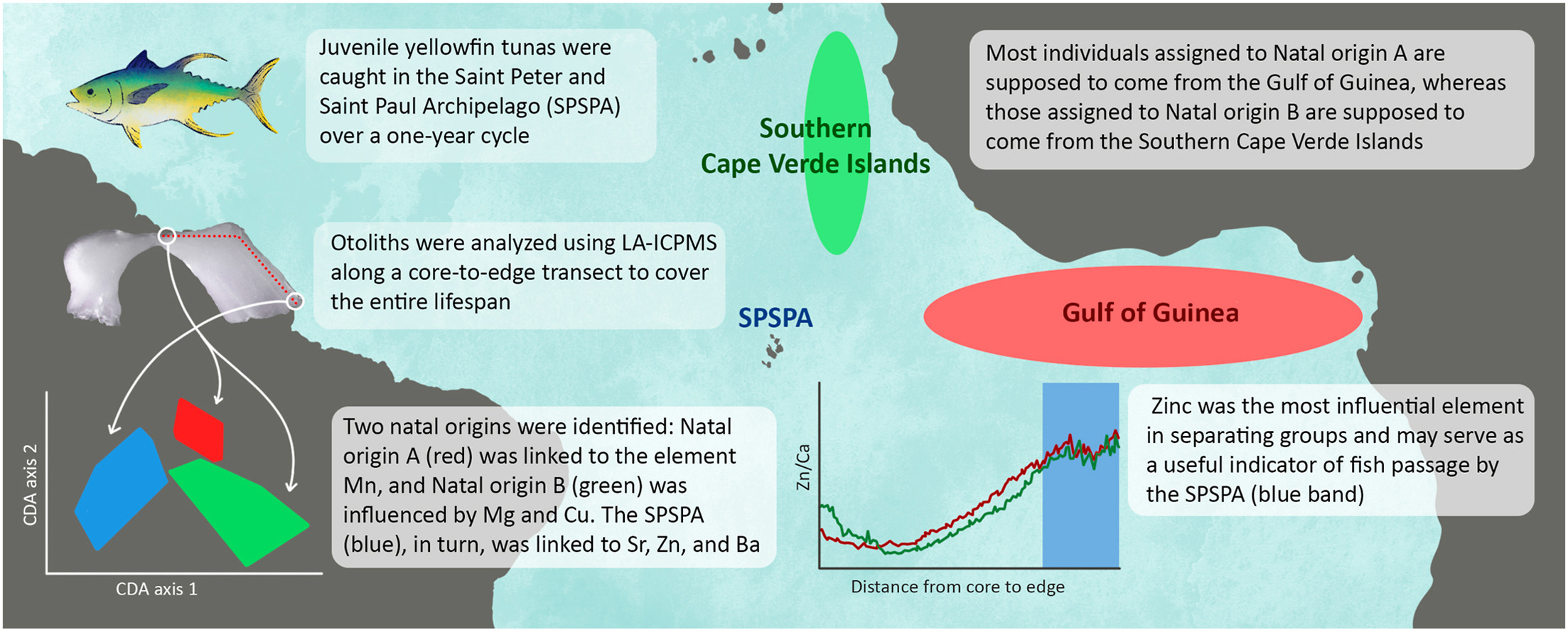
The Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago (SPSPA) is a small, remote group of islands on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that is home to many large-bodied