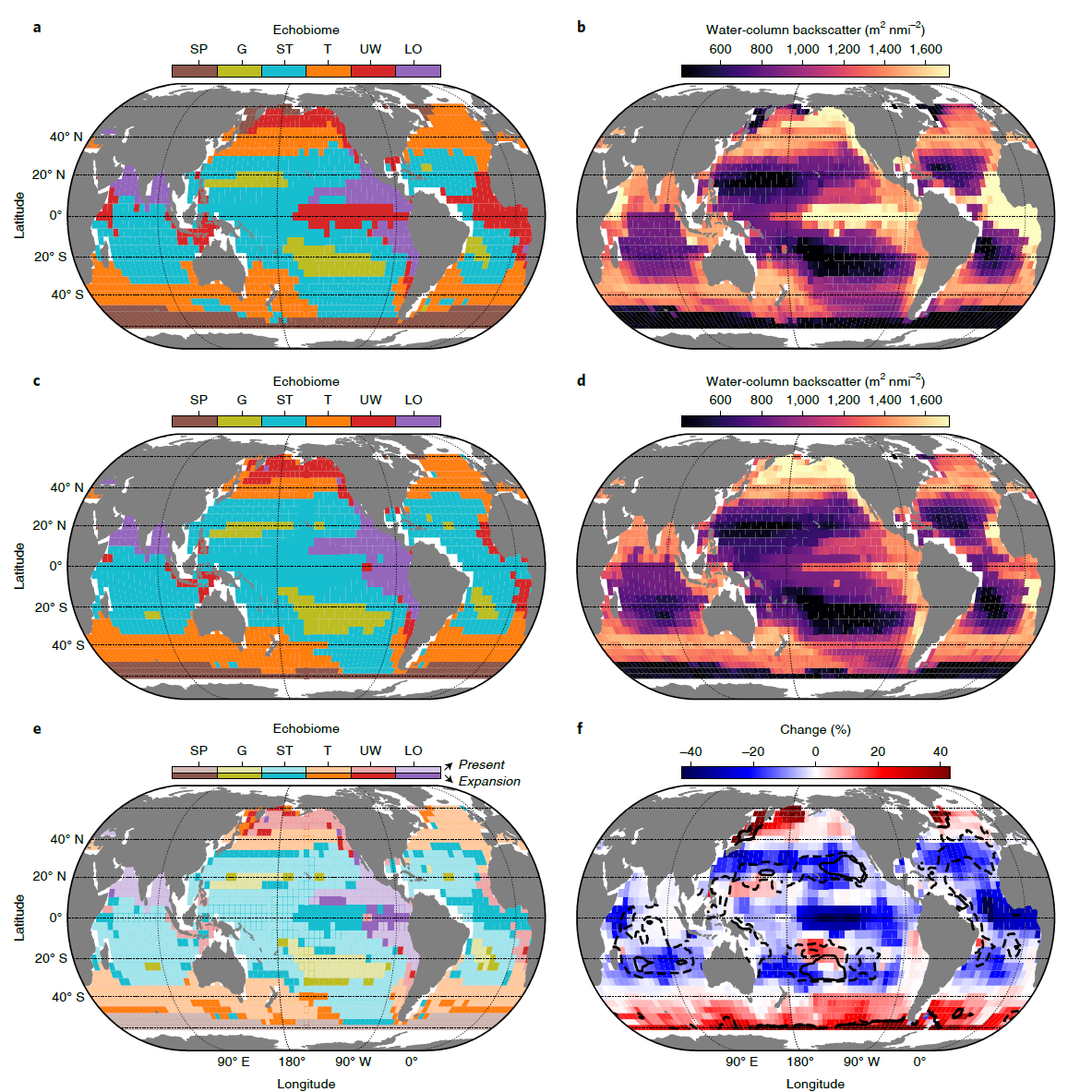
Pelagic fauna is expected to be impacted under climate change according to ecosystem simulations. However, the direction and magnitude of the impact is still uncertain
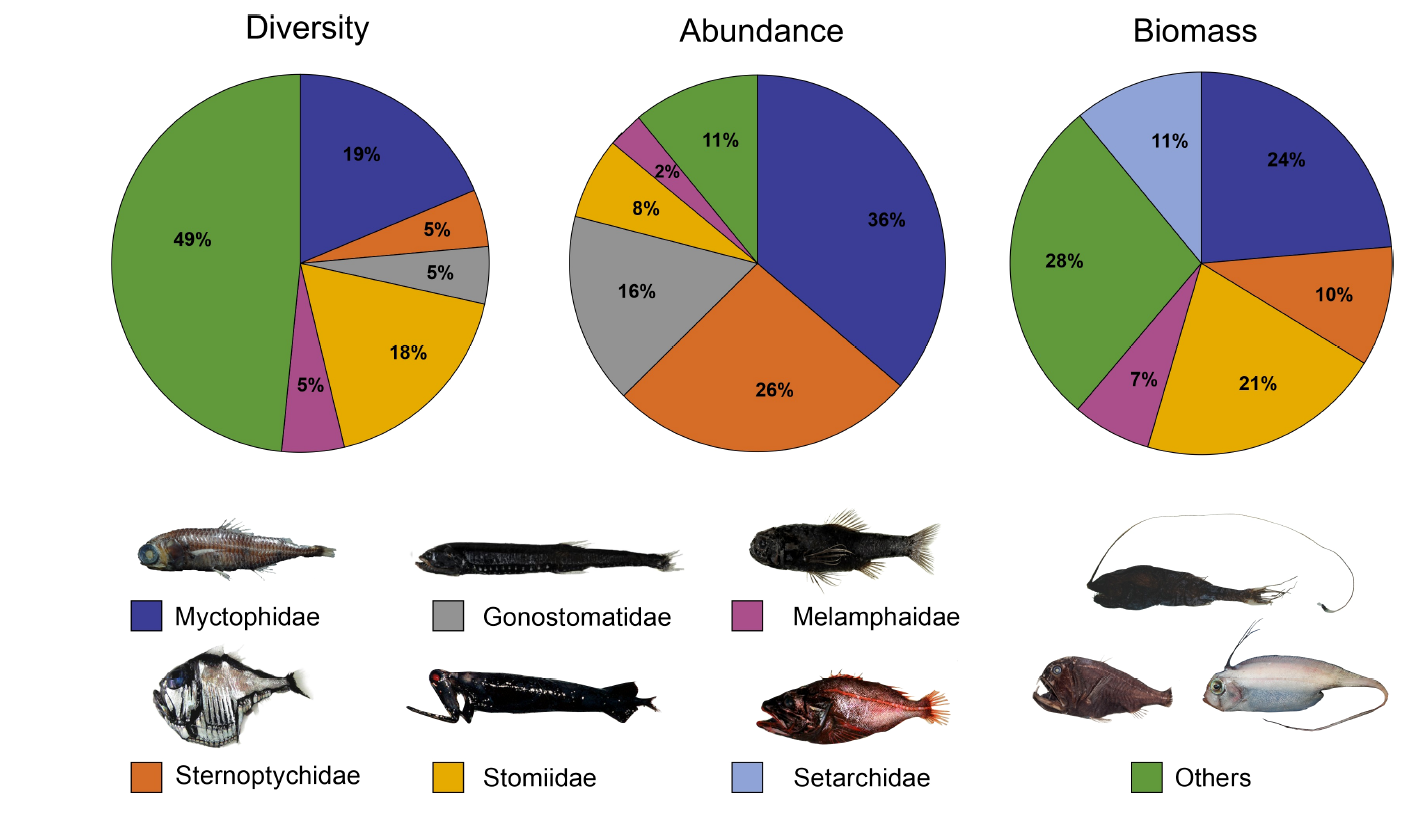
Mesopelagic fishes play critical ecological roles by sequestering carbon, recycling nutrients, and acting as a key trophic link between primary consumers and higher trophic levels.
Tropical marine ecosystems are highly biodiverse and provide resources for small-scale fisheries and tourism. However, precise information on fish spatial distribution is lacking, which limits
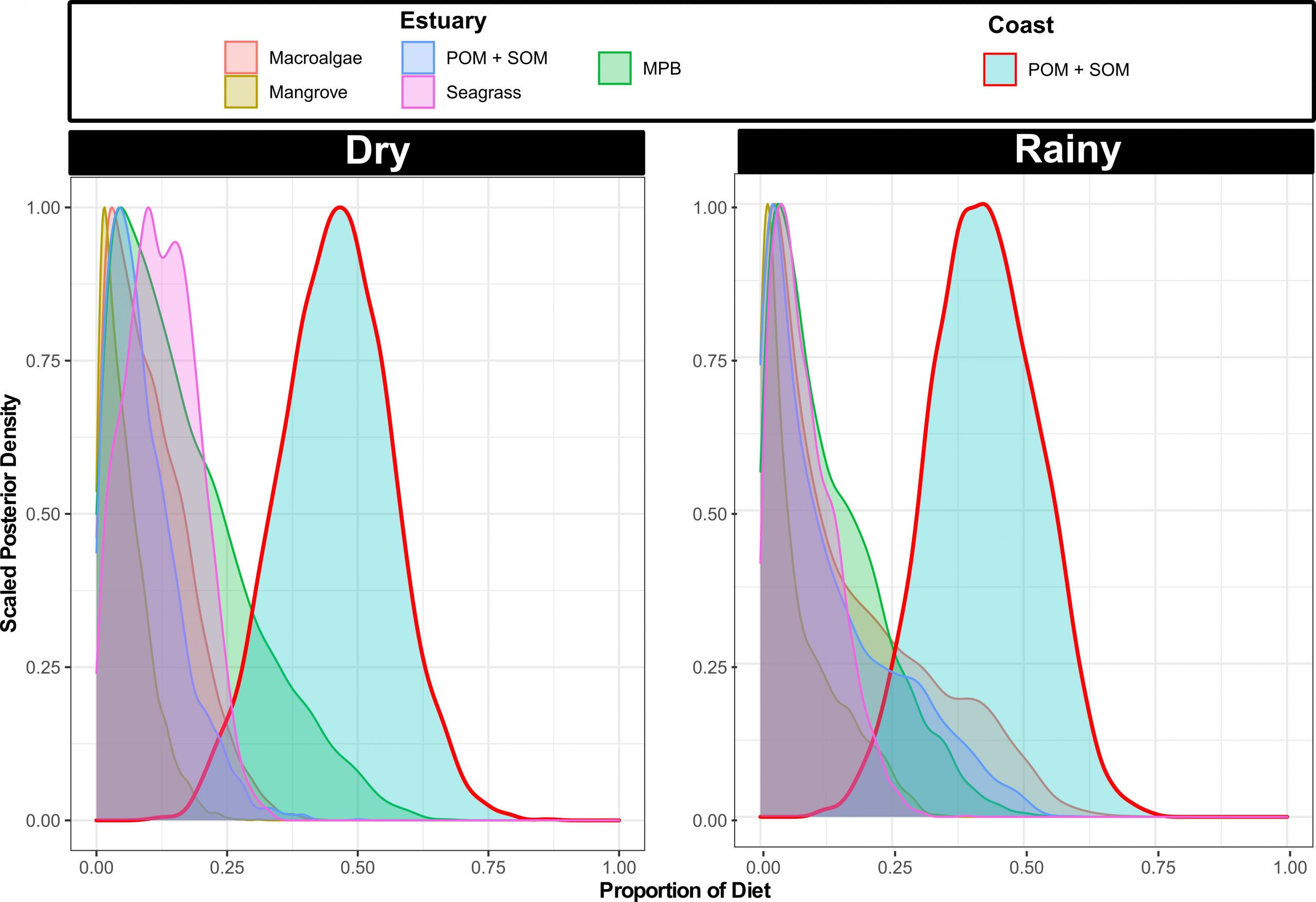
The lack of knowledge about highly anthropised tropical ecosystems poses a problem for their conservation. Using carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes, we studied the food
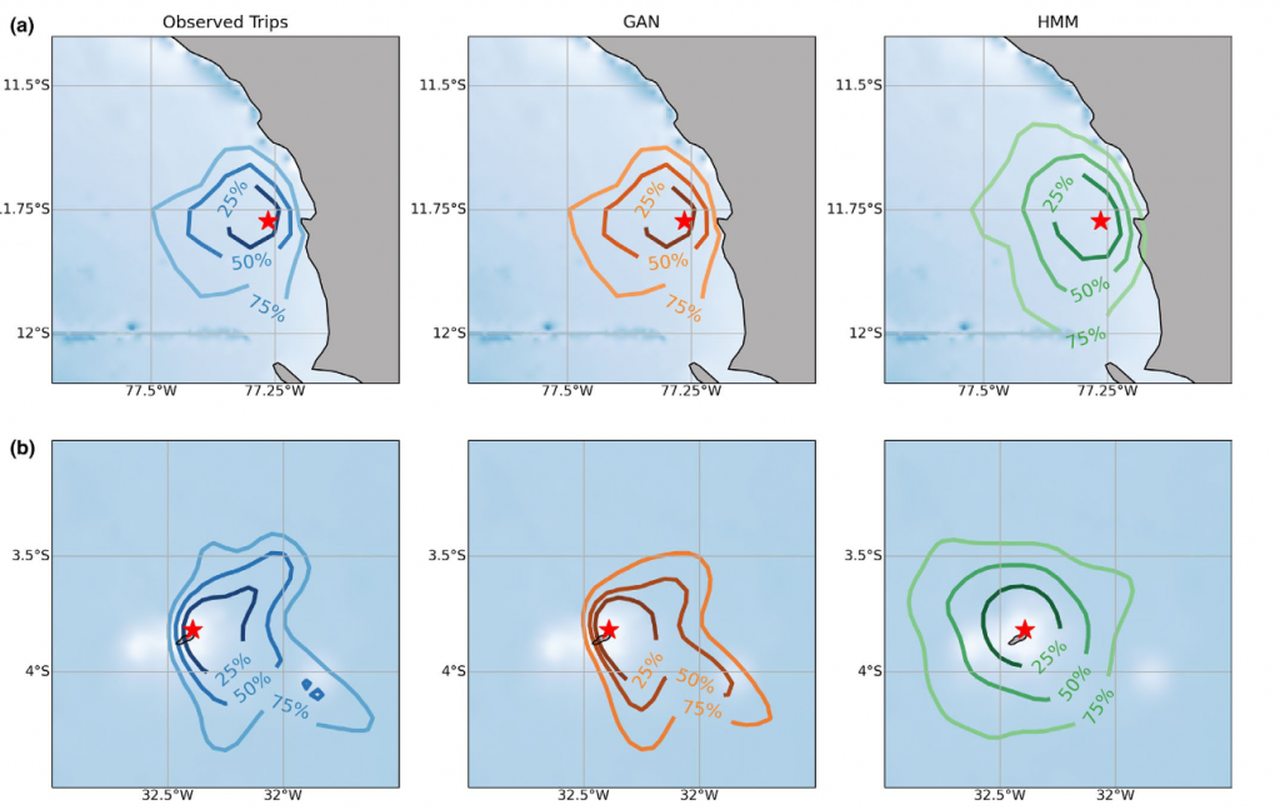
relatively large amounts of animal trajectories. Modelling such trajectories may contribute to explaining the mechanisms underlying observed behaviours and to clarifying ecological processes at the
Microplastics (MPs) are widely distributed in marine ecosystems, and their ubiquitous presence is raising concern, particularly about possible impacts on fisheries resources. In tropical regions,
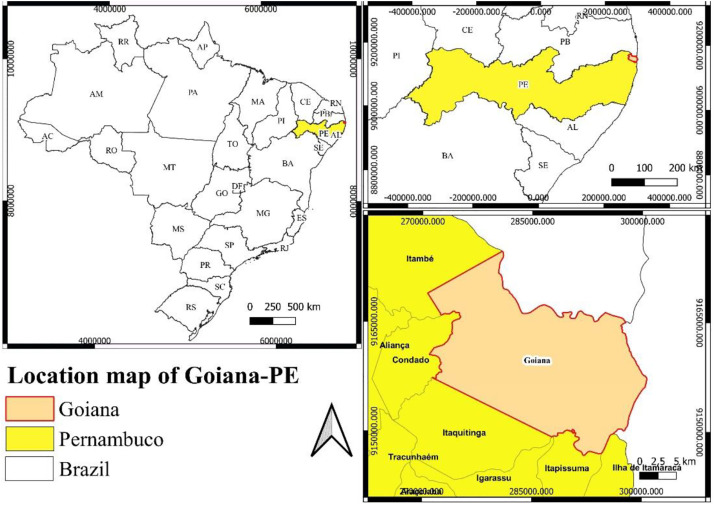
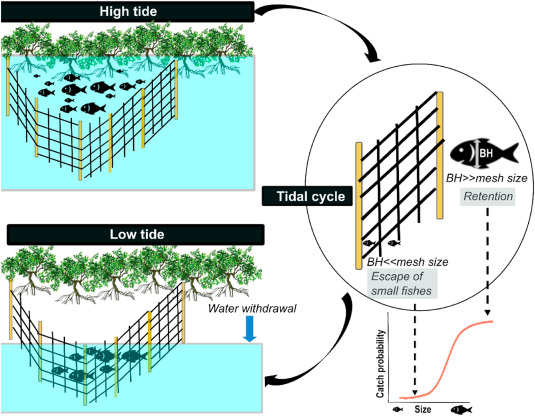
For centuries, intertidal fishing in mangroves using block nets has been of socio-economic and cultural importance to many tropical fishing communities. However, data characterising these
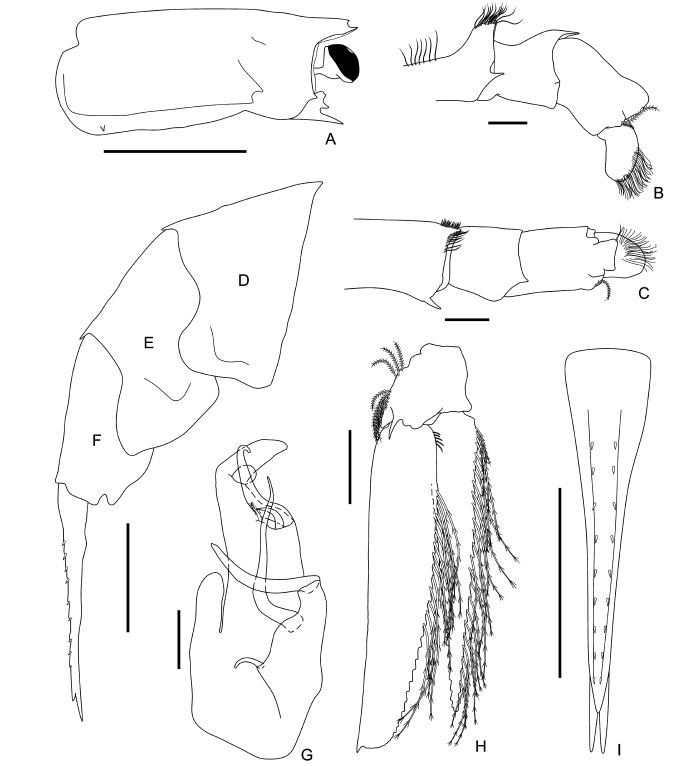
Euphausiids are a diverse order of crustaceans that play a key role in pelagic food webs. The genus Thysanopoda H. Milne Edwards, 1830 is composed
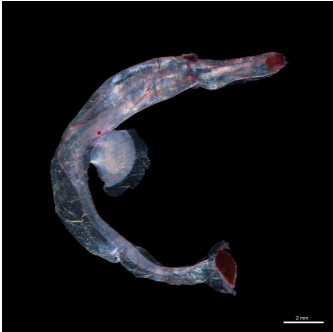
Biogeographic and taxonomic knowledge on planktonic mollusks, specifically on Pterotracheoidea (also known as heteropods or sea elephants) in tropical oceans, is still incomplete. In this
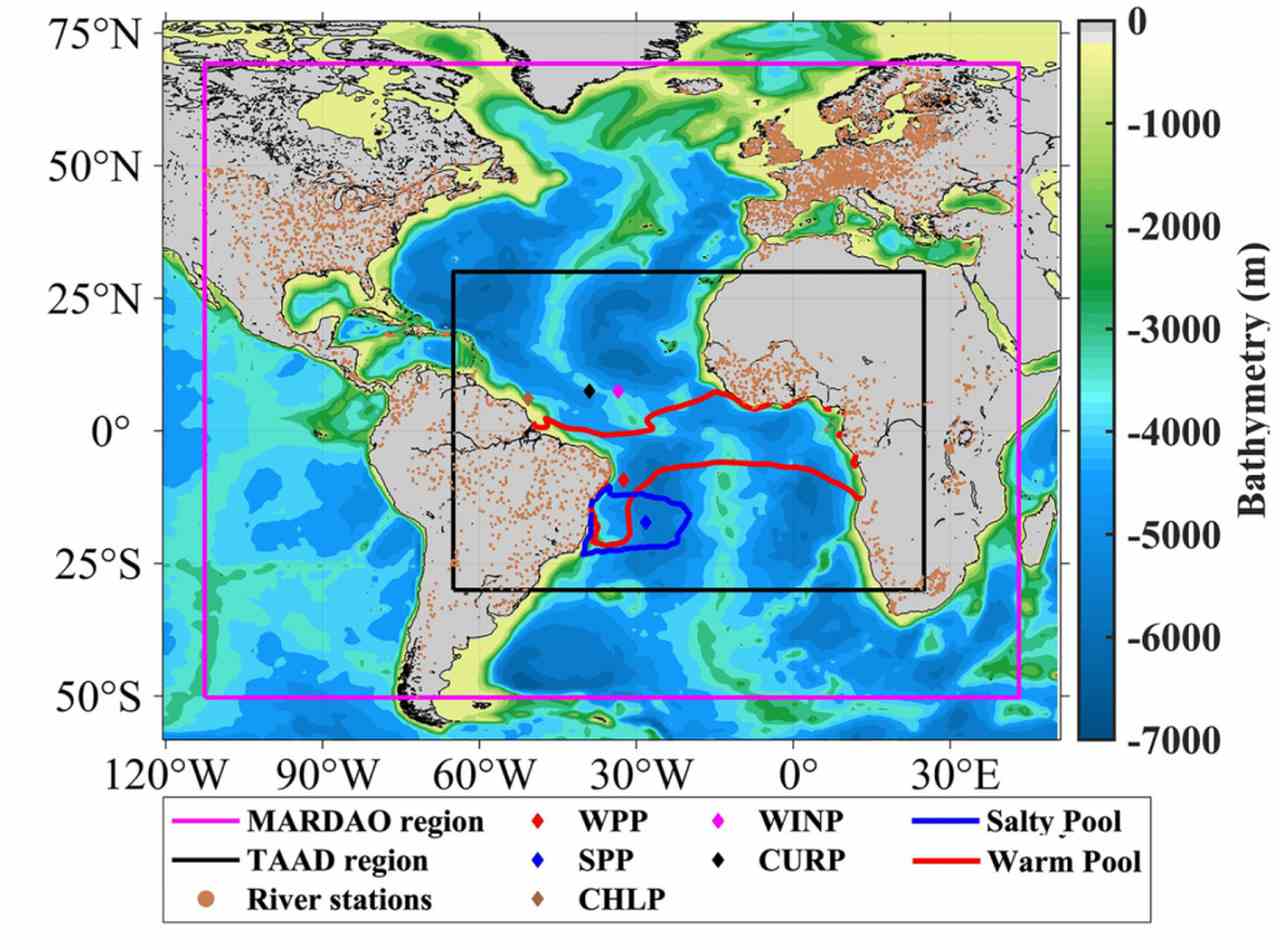
The Tropical Atlantic Ocean Database and Monthly Anomalies of River Discharge on Atlantic Ocean datasets encompass the monthly anomalies of a variety of physical, biogeochemical